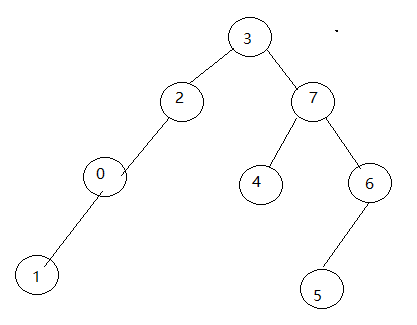
03-树 2 List Leaves 题目要求 Given a tree, you are supposed to list all the leaves in the order of top down, and left to right.
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤10) which is the total number of nodes in the tree – and hence the nodes are numbered from 0 to N −1. Then N lines follow, each corresponds to a node, and gives the indices of the left and right children of the node. If the child does not exist, a “-“ will be put at the position. Any pair of children are separated by a space.
Output Specification: For each test case, print in one line all the leaves’ indices in the order of top down, and left to right. There must be exactly one space between any adjacent numbers, and no extra space at the end of the line.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 8 1 - - - 0 - 2 7 - - - - 5 - 4 6
Sample Output: Solution: 题目要求通过输入节点数以及每个节点的左儿子和右儿子,从上到下打印出叶节点。解题的关键是通过层序遍历找到叶子结点去输出。
根据题意搭建程序框架:
1 2 3 4 int main () 输入建立二叉树 寻找叶子结点并输出 }
程序的框架较为简单,只需要两个函数就可以完成题目要求,接下来分析两个函数的实现方法。
① 输入建立二叉树函数
根据题目的输入要求,我们可以使用静态链表即结构体数组的方式来存储二叉树。
1 2 3 4 5 struct treeNode { char data; int left; int right; }T[10 ];
输入的第几行就是代表该节点的值为几。例如样例输入中第 0 行的 1 -代表值为 0 的节点左孩子的值为 1,即指向第 1 行,右孩子为空(-1),建树应该是这样:
二叉树根结点的位置不一定位于输入的第一行,因此在建二叉树的过程中,找出所建二叉树的根结点很关键。我们在建树的过程中寻找根结点的位置就可以通过遍历结构体数组中左右子树指向的下标,缺少的那个下标即是根结点所在下标。遍历的方法可以是创建一个 check[] 数组,初始化所有位置数值都为 0,然后在所有输入的左右子树的下标对应的 check[] 数值记为 1,最后遍历 check[] 数组找到数值为 0 的下标即是根结点所在位置。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 int buildTree (Tree t[]) int root = -1 ; cin >> N; char l, r; int check[10 ] = {0 }; for (int i=0 ; i<N; i++) { t[i].data = i; cin >> l >> r; if (l != '-' ) { t[i].left = l - '0' ; check[t[i].left] = 1 ; } else t[i].left = -1 ; if (r != '-' ) { t[i].right = r - '0' ; check[t[i].right] = 1 ; } else t[i].right = -1 ; } for (int i=0 ; i<N; i++) { if (!check[i]) { root = i; break ; } } return root; }
② 层序遍历打印叶子节点的函数
要按照从上到下,从左到右的顺序找到并输出叶子结点就要应用到层序遍历二叉树的方法,层序遍历就要用到队列,我这里选择直接调用 STL 的 队列(queue),而没有自己手写队列操作。
首先建立一个保存叶子结点的数组,初始化每个叶子结点为 -1。首先建立队列,将二叉树根结点入队。接着在队列非空时,执行层序遍历操作,若队首元素的左右孩子全部为空,则说明其是叶子结点,将他存入 leaves 数组中;若其子树非空,按照先左后右的顺序入队,然后队首元素出队,直至队列为空,则遍历完毕。
最后控制输出,因为输出的叶子结点之间都有空格,可以看做除了第一个元素外,都是输出“空格 + 叶子结点”,只需要设置标记将第一个输出的元素找到不输出空格就好。然后遍历输出 leaves 数组,即可得到结果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 void PrintLeaves (int r, int n) int leaves[10 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; ++i) { leaves[i] = -1 ; } int k = 0 ; int i; bool isFirst = 1 ; queue<int > Q; Q.push (r); while (!Q.empty ()) { i = Q.front (); Q.pop (); if (T[i].left == -1 && T[i].right == -1 ) leaves[k++] = T[i].data; if (T[i].left != -1 ) Q.push (T[i].left); if (T[i].right != -1 ) Q.push (T[i].right); } int j = 0 ; while (leaves[j] != -1 ) { if (!isFirst) cout << " " ; cout << leaves[j++]; isFirst = 0 ; } cout << endl; }
Code: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef struct treeNode Tree ;struct treeNode { char data; int left; int right; }T[10 ]; int N; int buildTree (Tree t[]) void PrintLeaves (int r, int n) int main () int r; r = buildTree (T); PrintLeaves (r,N); return 0 ; } int buildTree (Tree t[]) int root = -1 ; cin >> N; char l, r; int check[10 ] = {0 }; for (int i=0 ; i<N; i++) { t[i].data = i; cin >> l >> r; if (l != '-' ) { t[i].left = l - '0' ; check[t[i].left] = 1 ; } else t[i].left = -1 ; if (r != '-' ) { t[i].right = r - '0' ; check[t[i].right] = 1 ; } else t[i].right = -1 ; } for (int i=0 ; i<N; i++) { if (!check[i]) { root = i; break ; } } return root; } void PrintLeaves (int r, int n) int leaves[10 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; ++i) { leaves[i] = -1 ; } int k = 0 ; int i; bool isFirst = 1 ; queue<int > Q; Q.push (r); while (!Q.empty ()) { i = Q.front (); Q.pop (); if (T[i].left == -1 && T[i].right == -1 ) leaves[k++] = T[i].data; if (T[i].left != -1 ) Q.push (T[i].left); if (T[i].right != -1 ) Q.push (T[i].right); } int j = 0 ; while (leaves[j] != -1 ) { if (!isFirst) cout << " " ; cout << leaves[j++]; isFirst = 0 ; } cout << endl; }